Blog
Understanding As-Built Drawings in the Telecom Industry

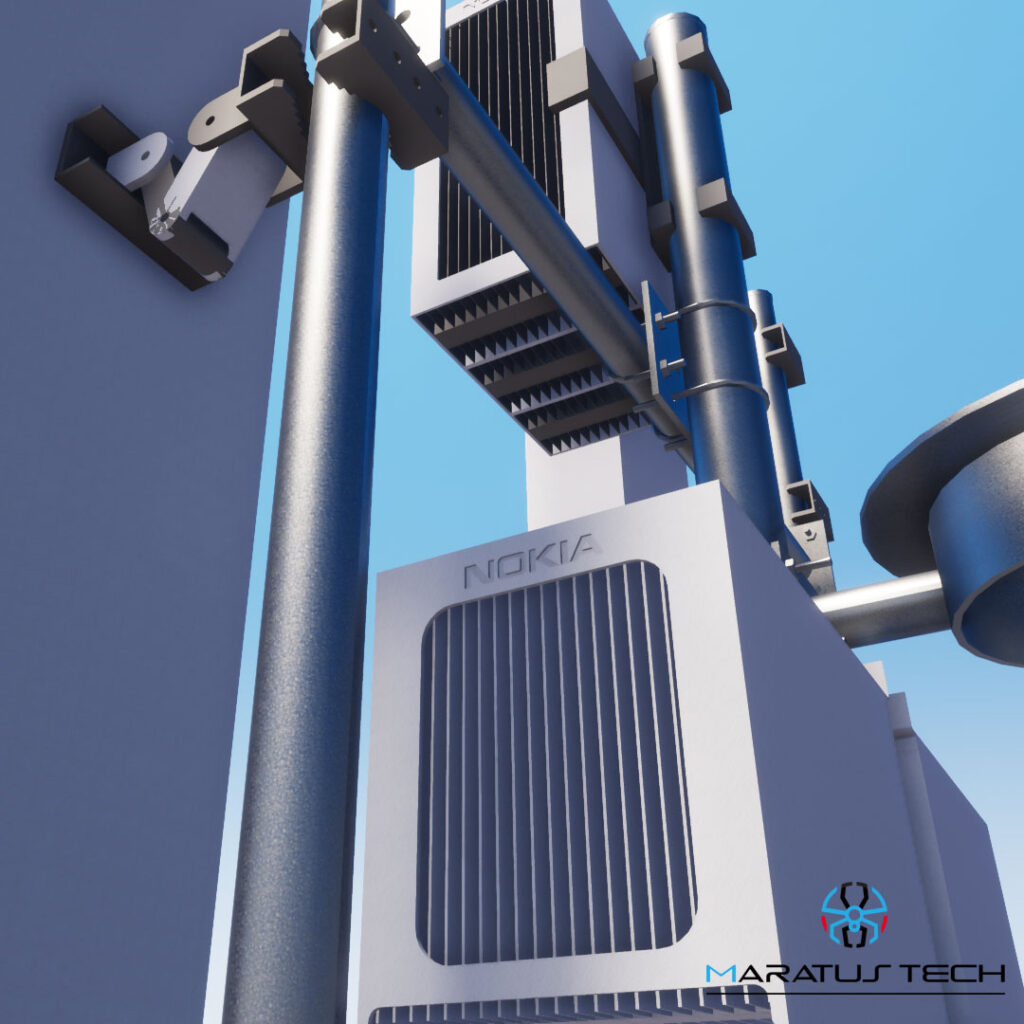
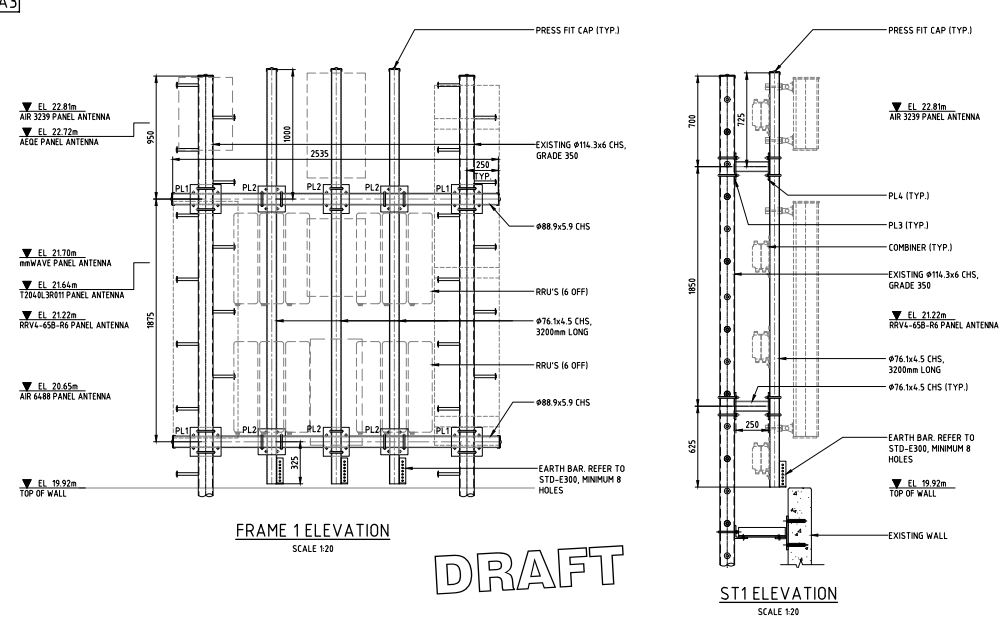
As-built drawings, also known as red-line drawings or record drawings, are essential documents in the telecom industry. They provide a detailed record of the actual construction and installation of telecom infrastructure, ensuring accuracy and facilitating future maintenance and upgrades1. In this blog post, we’ll explore what as-built drawings are, their importance, and the process of creating them.
Body: As-built drawings are created at the end of a construction project and include a revised set of drawings that compare the original specifications against the final specifications. These drawings document any modifications, design changes, extra works, and field changes made during the construction process1. They are crucial for maintaining accurate records of the installed infrastructure and ensuring that future modifications or maintenance work can be carried out efficiently.
Key Considerations:
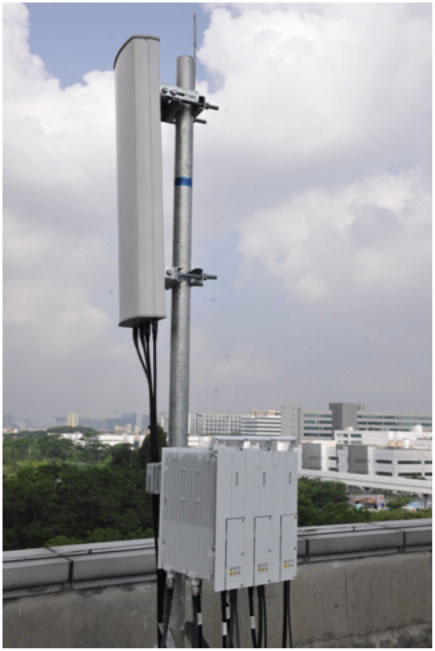
- Accuracy: As-built drawings must accurately reflect the final installed state of the telecom infrastructure. This includes all equipment, cabling, and connections.
- Compliance: Adhering to industry standards and regulations is essential for safety and functionality. This includes meeting local building codes and telecom-specific requirements.
- Detail: The drawings should include detailed information about the location of key components, such as shut-off valves, cables, and equipment.
- Documentation: As-built drawings should be updated with any last-minute alterations and changes, and the revision date and number should always be noted.
Best Practices:
- Site Surveys: Conduct thorough site surveys to understand the terrain, environmental conditions, and potential obstacles.
- Material Selection: Choose high-quality materials that offer durability and low maintenance requirements.
- Modular Designs: Implement modular designs that allow for easy assembly, disassembly, and expansion.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections to identify and address any structural issues before they affect network performance.
Use Cases:
- Maintenance and Repairs: As-built drawings provide essential information for future maintenance and repairs, ensuring that technicians can quickly locate and address issues.
- Upgrades and Expansions: Accurate as-built drawings facilitate future upgrades and expansions by providing a clear reference for the existing infrastructure.
- Safety Management: Detailed drawings help identify potential safety hazards and ensure proper safety measures are in place.
Conclusion: As-built drawings are a critical component of the telecom industry, providing accurate documentation of installed infrastructure and ensuring efficient maintenance and future upgrades. By following best practices and maintaining detailed records, telecom operators can ensure the reliability and longevity of their networks.