Blog
Optimizing Feeder Management Through Standard Gland Plates in Telecom Sites
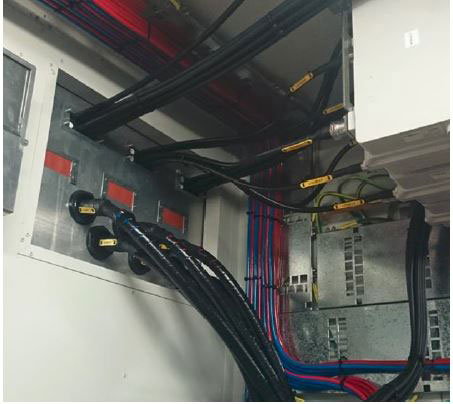

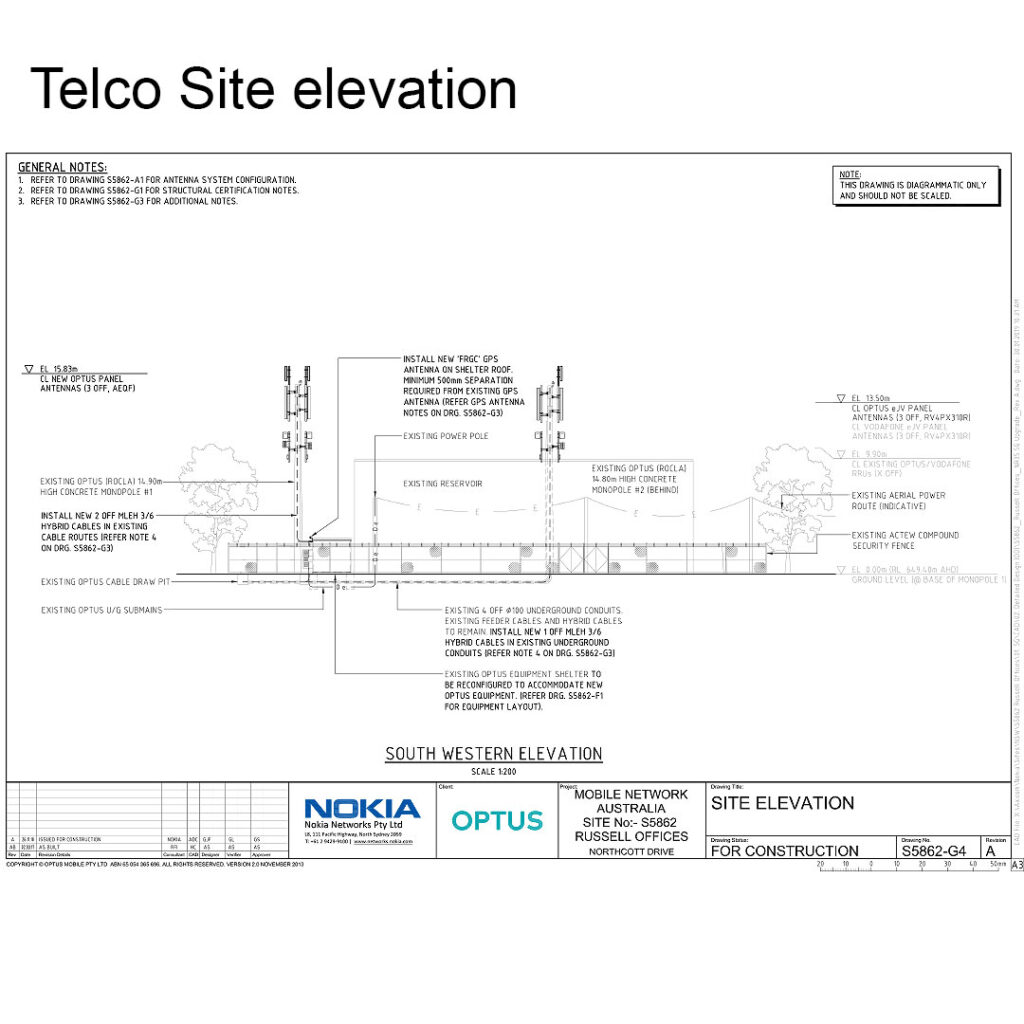
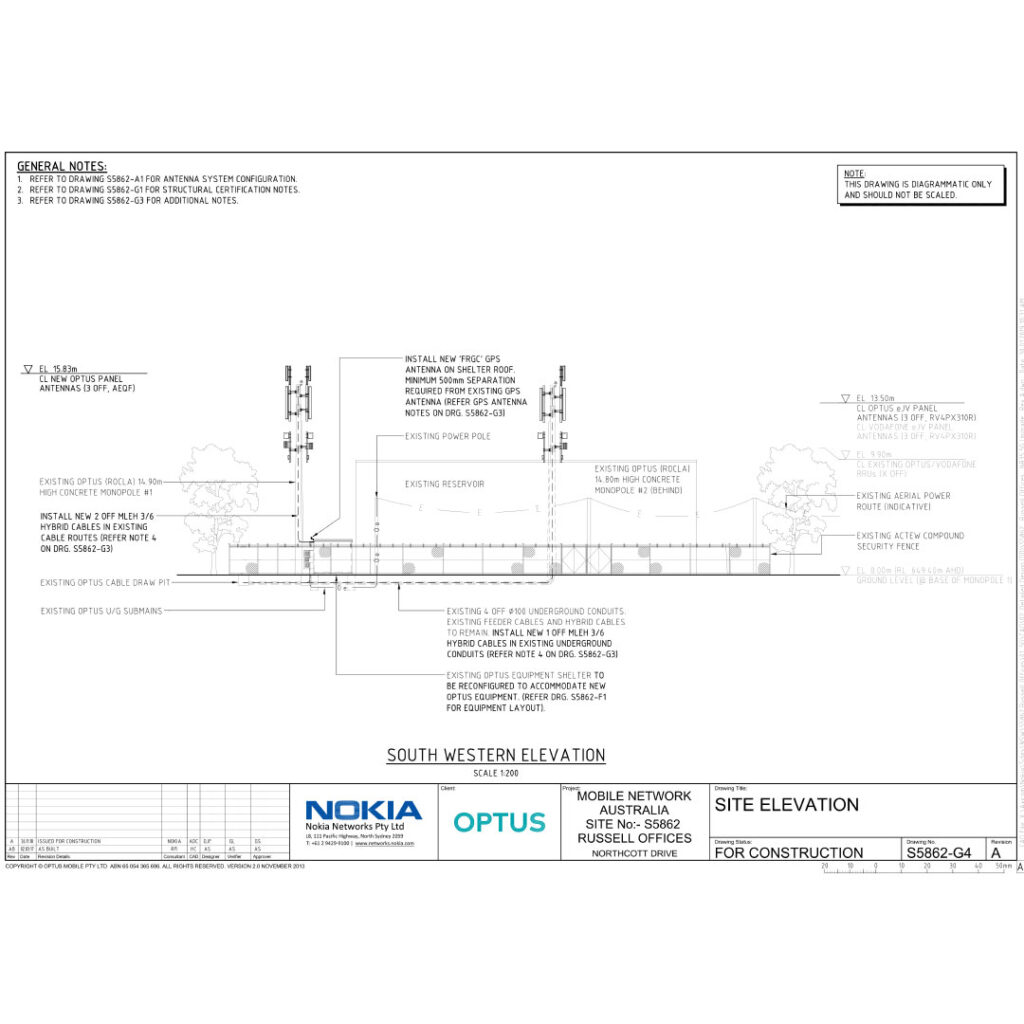
In telecom sites, efficiently managing the maximum number of feeders through a standard gland plate is critical for maintaining both operational efficiency and safety standards. This comprehensive guide delves into essential considerations, best practices, and technical guidelines for optimizing gland plate use in telecom infrastructure.
Understanding Gland Plates
Definition: A gland plate serves as a secure and organized entry point for cables and feeders in telecom sites, protecting connections and maintaining cable integrity.
Purpose:
- Organize cable entries.
- Protect cables from damage.
- Ensure secure and sealed connections.
Key Considerations for Maximizing Feeders
1. Gland Plate Size and Type:
- Standard Sizes: Gland plates typically come in standard sizes such as 300×300 mm, 400×400 mm, and 600×600 mm. Selecting the appropriate size depends on the number and diameter of feeders to be accommodated.
- Material Selection: Opt for durable materials such as stainless steel or galvanized metal to ensure long-lasting protection.
2. Cable Specifications:
- Compatibility: Ensure feeders are compatible with the gland plate regarding diameter and specifications.
- Avoid Bundling: Prevent bundling too many cables together to avoid interference and potential damage.
3. Environmental Protection:
- Sealing: Implement proper sealing techniques to guard against moisture, dust, and other environmental factors.
- IP Rating: Select gland plates with suitable Ingress Protection (IP) ratings for the installation environment.
4. Safety Standards:
- Compliance: Adhere to relevant safety standards and regulations.
- Fire Resistance: Use fire-resistant materials and designs to enhance site safety.
Best Practices for Feeder Management
1. Accurate Planning and Measurement:
- Feeder Count: Precisely count and plan the number of feeders to prevent overloading the gland plate.
- Clear Labeling: Clearly label each feeder for easy maintenance and troubleshooting.
2. Proper Installation Techniques:
- Spacing: Maintain adequate spacing between feeders to prevent signal interference and physical damage.
- Secure Fastening: Ensure all feeders are securely fastened to avoid movement and strain on cables.
3. Regular Maintenance and Inspection:
- Periodic Checks: Conduct regular inspections to identify and rectify wear and tear or damage.
- Cleaning: Keep the gland plate and its surroundings clean to prevent dirt and debris buildup.
4. Use of Accessories:
- Grommets and Bushings: Utilize grommets and bushings for additional protection and to reduce cable wear.
- Cable Trays and Conduits: Implement cable trays and conduits for enhanced cable management and organization.
Conclusion
Effectively managing the maximum number of feeders through a standard gland plate is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and safety of telecom sites. By adhering to the key considerations and best practices outlined in this guide, telecom operators can optimize cable management and maintain a secure, reliable infrastructure.