Blog
A Comprehensive Guide to EME Plume Diagrams in the Telecom Industry

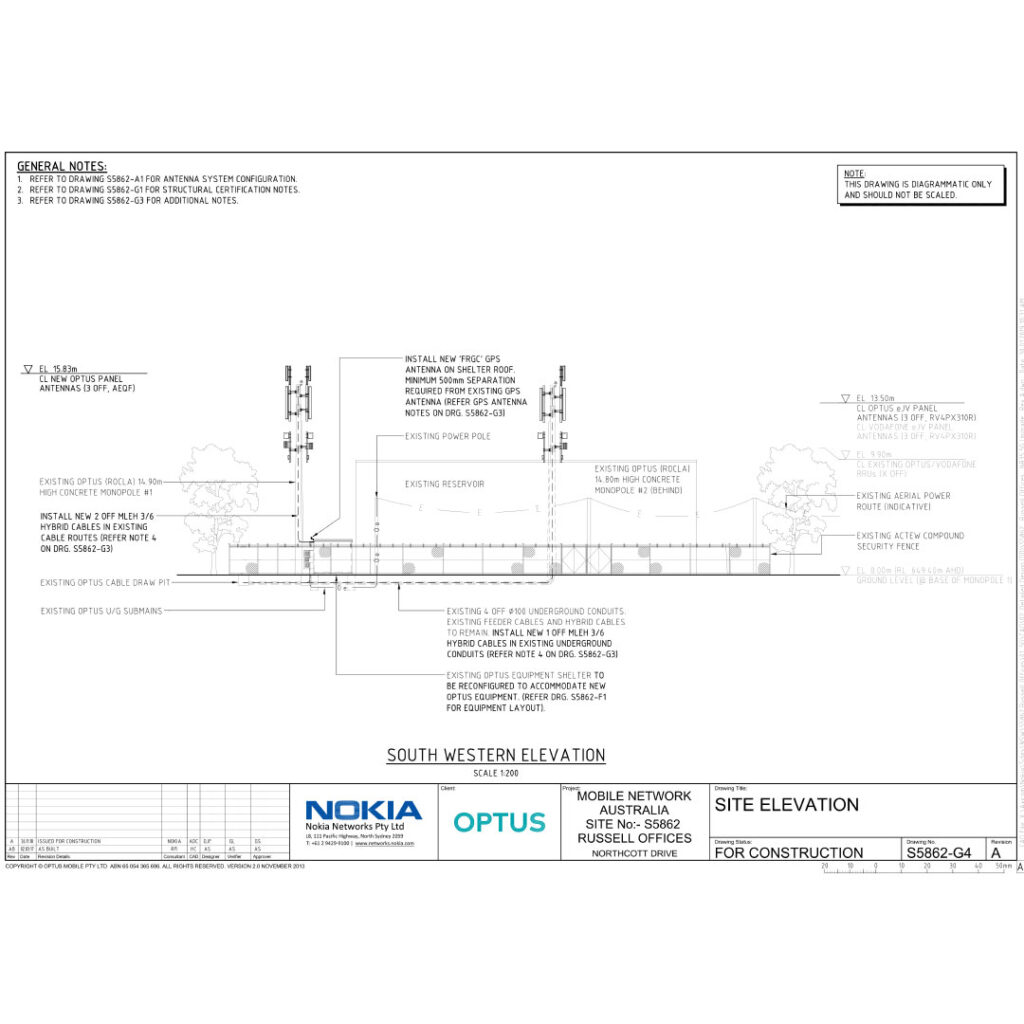
Electromagnetic Energy (EME) plume diagrams are essential tools in the telecom industry, used to visualize and manage radiation exposure levels around telecom sites. Understanding how to create and interpret these diagrams is crucial for ensuring safety and compliance. In this guide, we’ll explore the key components, best practices, and regulatory considerations for EME plume diagrams.
What is an EME Plume Diagram?
Definition: An EME plume diagram is a graphical representation that shows the distribution and intensity of electromagnetic energy emissions from telecom equipment. These diagrams help visualize the areas of potential exposure and ensure that radiation levels are within safe limits.
Purpose: The primary purpose of EME plume diagrams is to:
- Ensure compliance with safety regulations.
- Identify areas with high radiation exposure.
- Plan the placement of telecom equipment to minimize EME impact.
Key Components of EME Plume Diagrams
- Radiation Source:
- Equipment Identification: Clearly identify the telecom equipment emitting electromagnetic energy, such as antennas and transmitters.
- Emission Levels: Indicate the emission levels of each piece of equipment.
- Exposure Zones:
- Safe Zones: Areas where radiation levels are within safe limits.
- Caution Zones: Areas where radiation levels approach safety thresholds.
- Exclusion Zones: Areas where radiation levels exceed safety limits and access should be restricted.
- Frequency Bands:
- Frequency Details: Specify the frequency bands of the emitted electromagnetic energy, as different frequencies have varying impacts on safety.
- Diagram Annotations:
- Labels and Legends: Provide clear labels and legends to help interpret the diagram.
- Scale: Include a scale to represent distances accurately.
Best Practices for Creating EME Plume Diagrams
- Accurate Data Collection:
- Conduct thorough measurements of electromagnetic emissions from all telecom equipment using calibrated instruments.
- Use Advanced Software:
- Utilize specialized software tools to create precise and detailed EME plume diagrams.
- Regular Updates:
- Update the diagrams regularly to reflect any changes in equipment or emission levels.
- Stakeholder Collaboration:
- Work with engineers, health and safety experts, and regulatory bodies to ensure the diagrams meet all requirements.
- Clear Communication:
- Ensure that the diagrams are easy to understand for all stakeholders, including non-technical personnel.
Regulatory Considerations
- Compliance with Standards:
- Adhere to national and international standards for electromagnetic radiation exposure, such as those set by the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) and local authorities.
- Permits and Documentation:
- Maintain detailed records of EME plume diagrams and related documentation for regulatory inspections and audits.
- Public Safety:
- Engage with the local community to educate them about EME safety and address any concerns.
Conclusion: EME plume diagrams are vital for managing radiation exposure and ensuring the safety of telecom sites. By following the key components, best practices, and regulatory considerations outlined in this guide, telecom operators can effectively manage EME emissions and comply with safety standards.