Blog
Structure Design in the Telecom Industry: Key Considerations and Best Practices
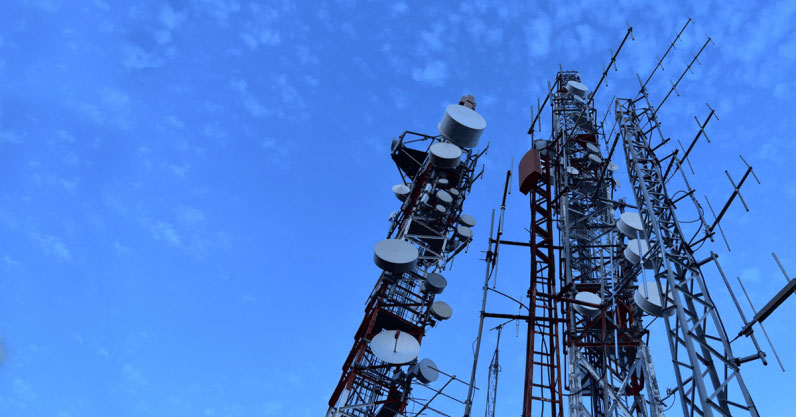
Effective structure design is a cornerstone of reliable and high-performance telecom networks. From tower installations to equipment housing, every aspect of telecom infrastructure plays a crucial role in ensuring seamless connectivity. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the key considerations and best practices for structure design in the telecom industry.
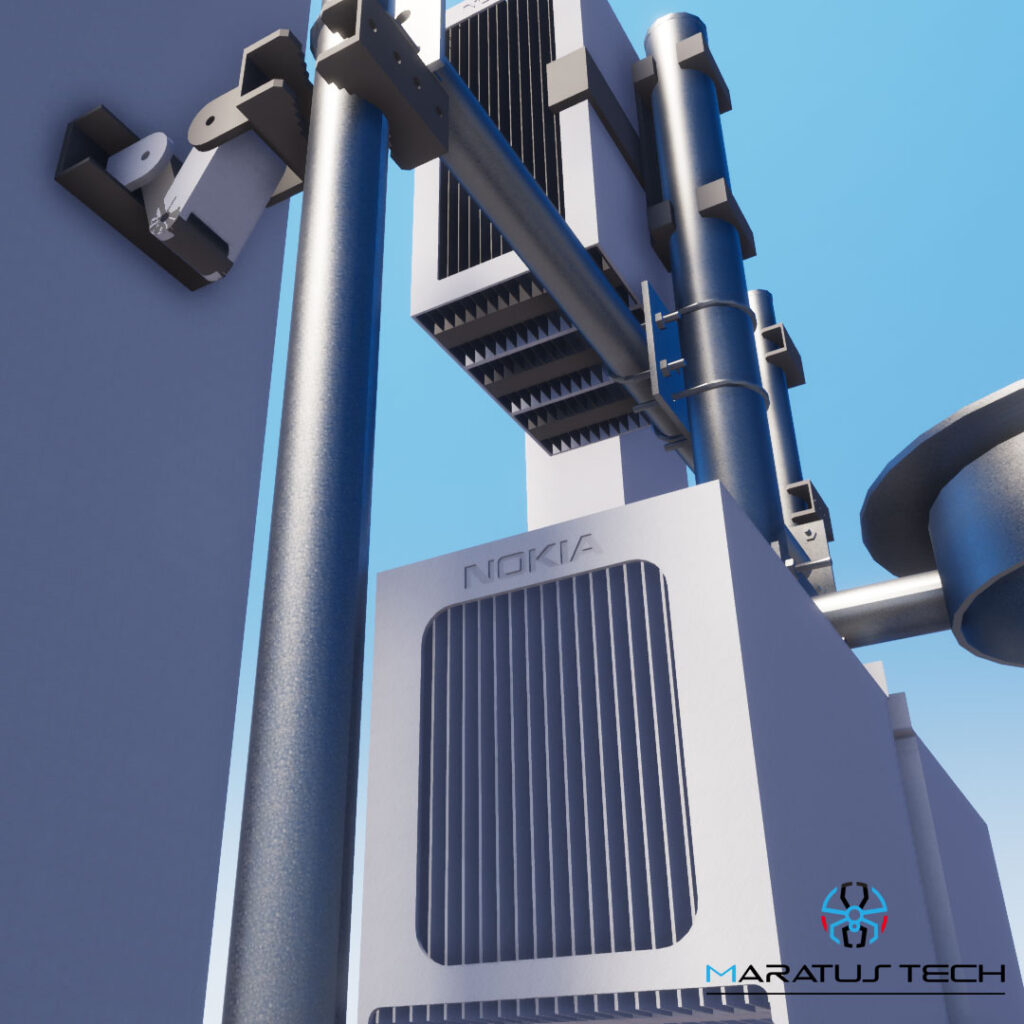
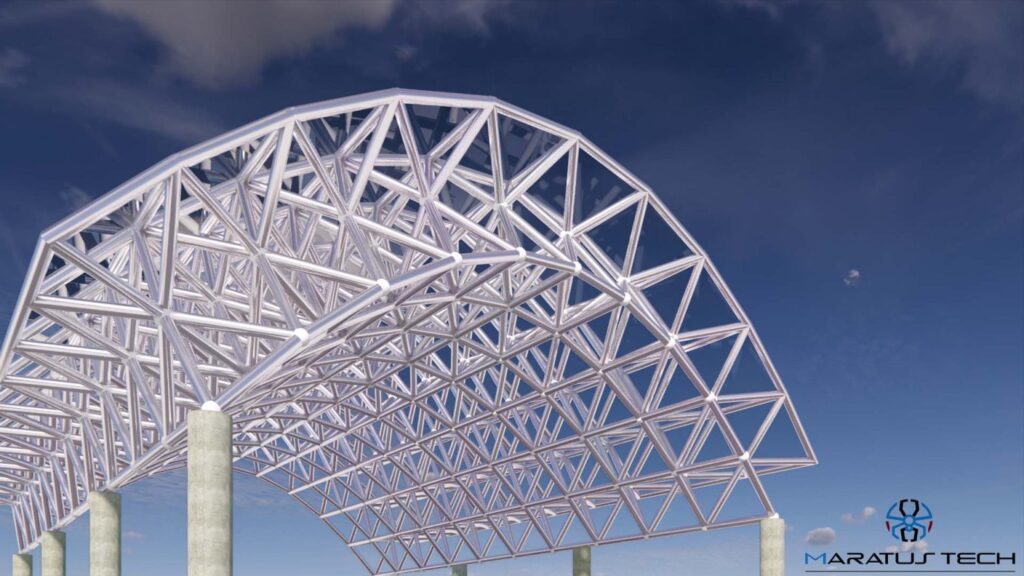
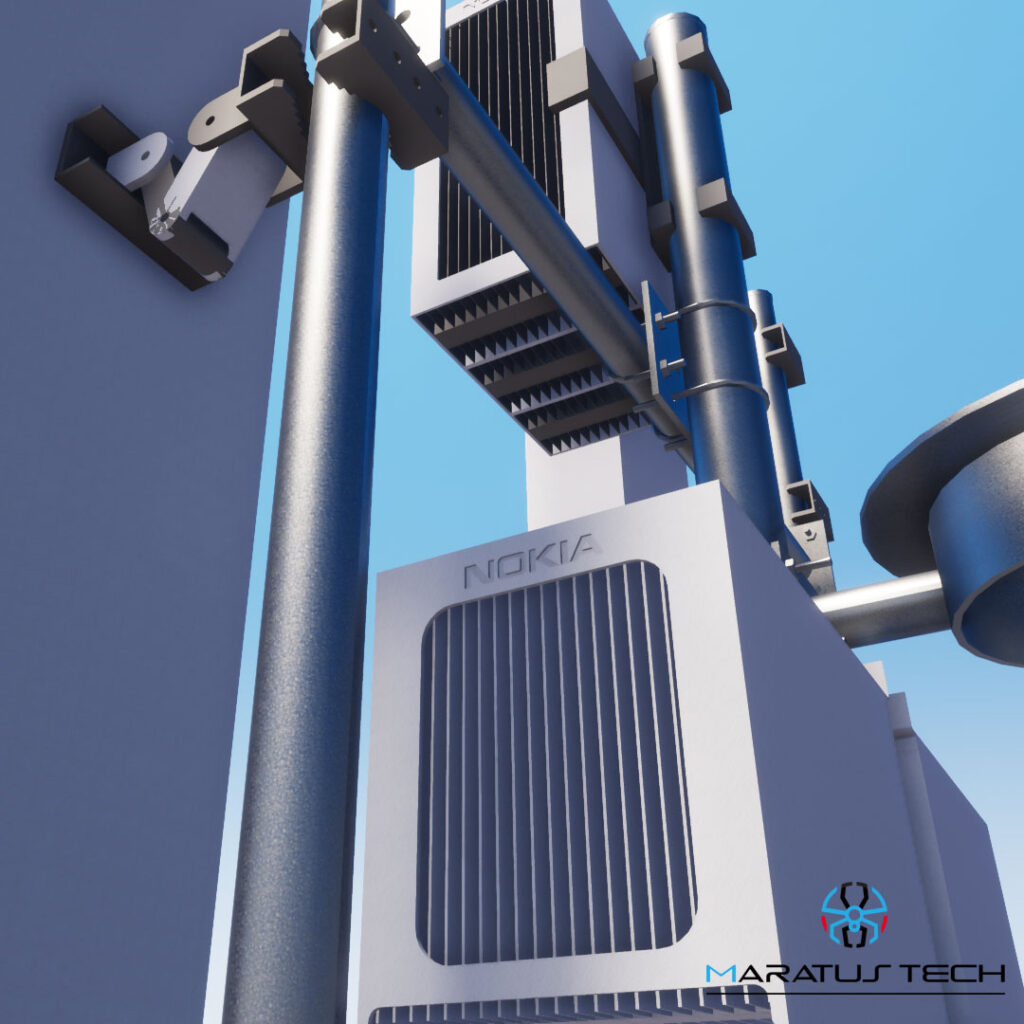
Body: Structure design in the telecom industry involves creating robust frameworks that support various network components such as antennas, base stations, and other equipment. These structures must withstand environmental challenges, ensure optimal performance, and facilitate easy maintenance.
Key Considerations:
- Structural Integrity: Ensuring that the design can withstand extreme weather conditions and heavy loads is paramount. Materials and construction methods should be chosen for their durability and strength.
- Compliance with Standards: Adhering to industry standards and regulations is essential for safety and functionality. This includes meeting local building codes and telecom-specific requirements.
- Scalability: Designing structures that can accommodate future expansions and technological upgrades helps in long-term network planning.
- Environmental Impact: Minimizing the environmental footprint of telecom structures is increasingly important. This includes selecting sustainable materials and practices.
- Accessibility and Maintenance: Designs should facilitate easy access for maintenance and upgrades, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Best Practices:
- Site Surveys: Conduct thorough site surveys to understand the terrain, environmental conditions, and potential obstacles.
- Material Selection: Choose high-quality materials that offer durability and low maintenance requirements.
- Modular Designs: Implement modular designs that allow for easy assembly, disassembly, and expansion.
- Use of Advanced Tools: Utilize advanced design tools and software to create precise and efficient structures.
- Regular Inspections: Schedule regular inspections to identify and address any structural issues before they affect network performance.
Use Cases:
- Urban Areas: Requires compact and efficient structures to fit within limited spaces while providing high capacity.
- Rural Deployment: Needs robust structures that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and extend network reach.
- Specialized Installations: Includes designs for unique environments like offshore platforms or high-altitude installations.
Conclusion: Effective structure design is critical to the success of telecom networks. By considering key factors such as structural integrity, compliance, scalability, and environmental impact, and following best practices, telecom operators can ensure their networks are reliable, efficient, and future-proof.
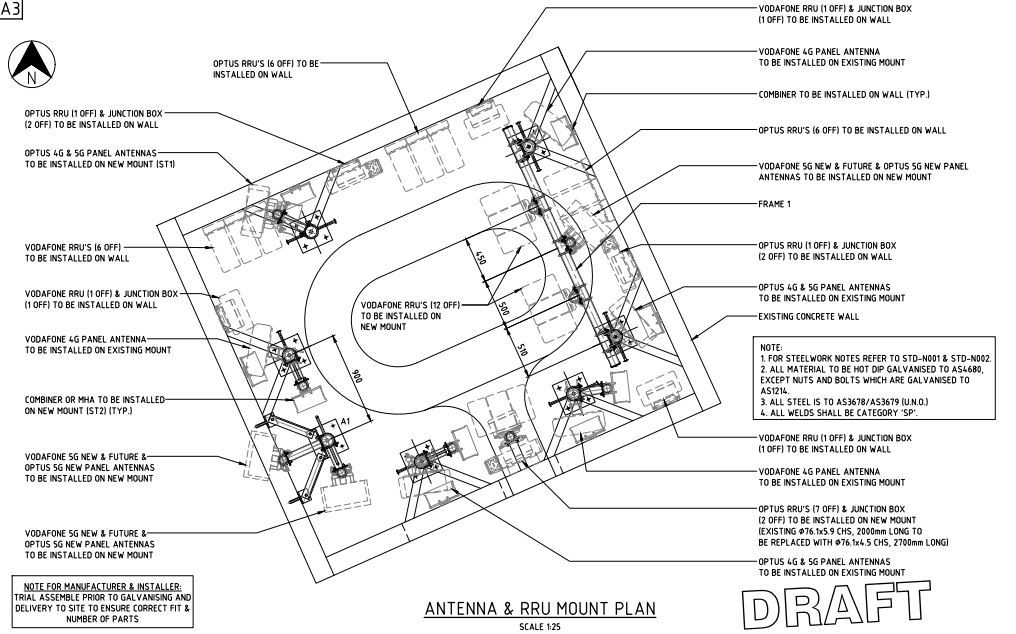
Plan
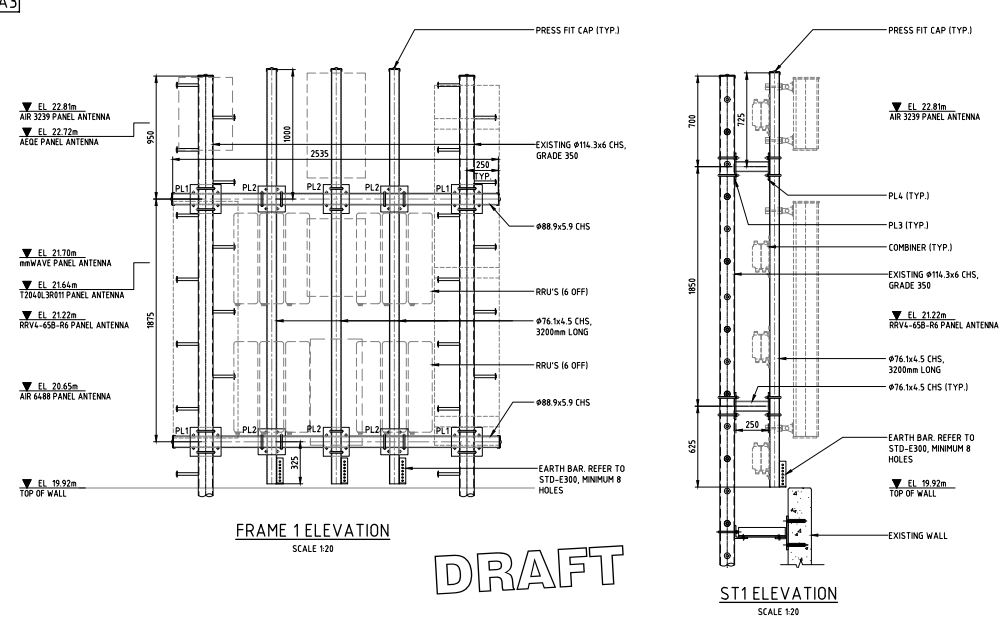
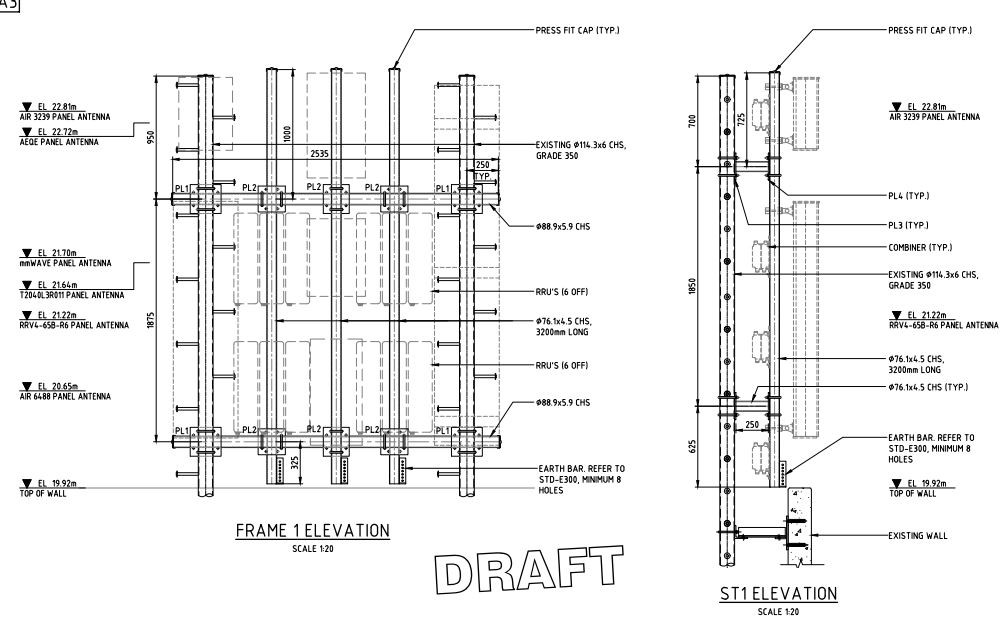
Elevation
Section
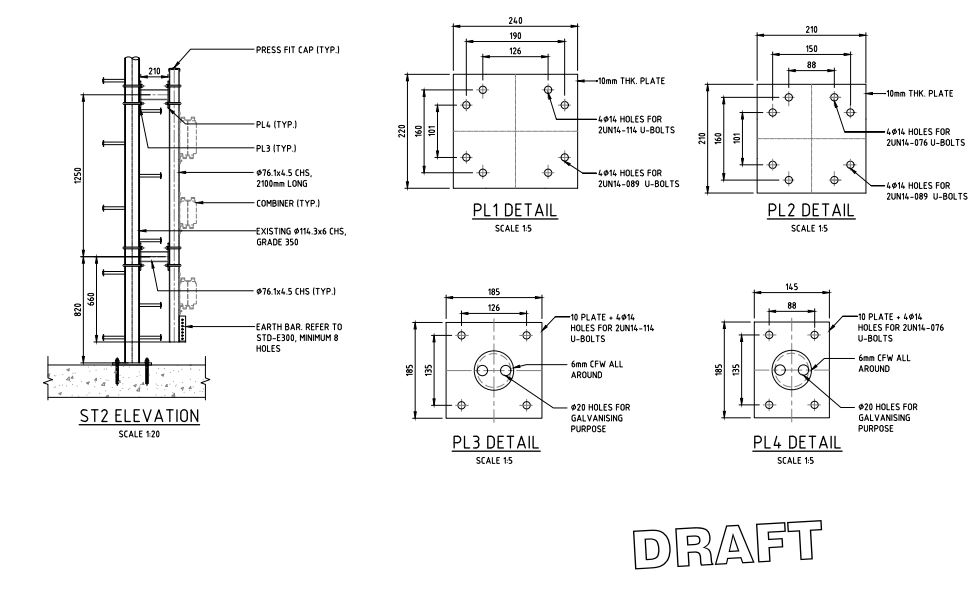
Details