Blog
Understanding GPS Antennas in the Telecom Industry

GPS antennas play a crucial role in the telecom industry, providing precise timing and synchronization essential for the smooth operation of communication networks. As networks become more complex and demand for high-speed connectivity grows, the importance of reliable GPS antennas cannot be overstated. In this blog post, we’ll dive into what GPS antennas are, their significance in the telecom sector, and how they contribute to network performance.
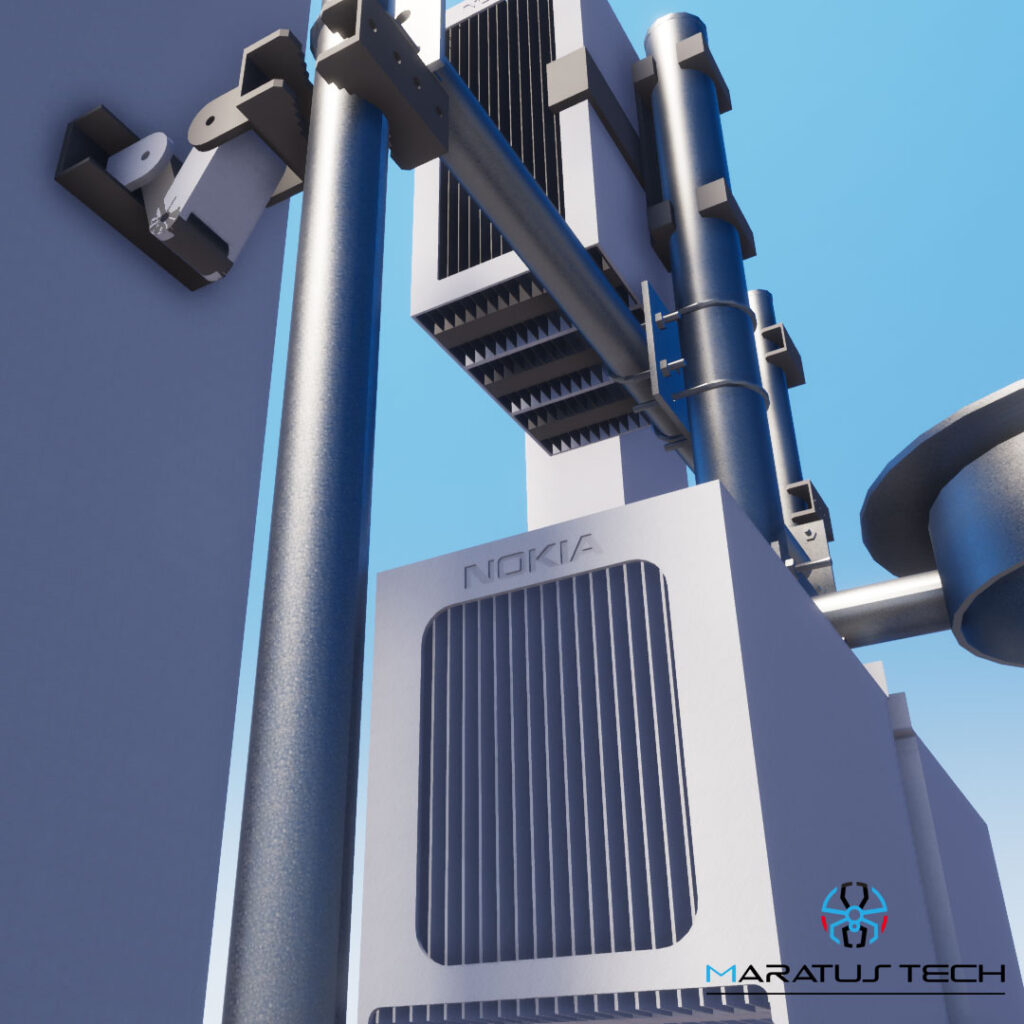
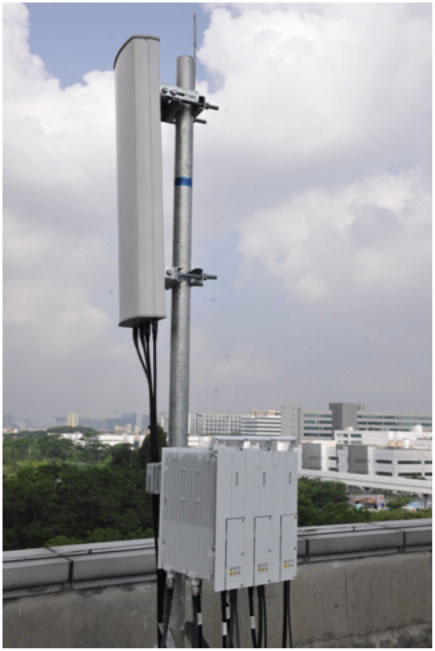
What is a GPS Antenna? A GPS antenna is a device that receives signals from Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites. These antennas are designed to capture the radio waves transmitted by satellites and convert them into electrical signals that can be processed by GPS receivers. In the telecom industry, GPS antennas are vital for providing accurate time and location data, which is critical for network synchronization and performance.
Importance in the Telecom Industry:
- Network Synchronization: GPS antennas provide precise timing information necessary for synchronizing various network components, ensuring seamless communication and data transfer.
- Enhanced Performance: Accurate timing helps prevent data loss and reduces latency, leading to improved network reliability and user experience.
- Cell Tower Coordination: GPS antennas help coordinate the operation of multiple cell towers, optimizing coverage and capacity in dense urban areas.
- Emergency Services: Reliable GPS data is crucial for location-based services, such as emergency response and E911, ensuring quick and accurate assistance.
Types of GPS Antennas:
- Active GPS Antennas: These antennas have built-in amplifiers that boost the signal strength, making them suitable for areas with weak signal reception.
- Passive GPS Antennas: These antennas do not have built-in amplifiers and rely on the GPS receiver to process the signals. They are typically used in areas with strong signal reception.
Factors to Consider:
- Location: The placement of a GPS antenna is critical for optimal performance. It should be installed in a location with a clear view of the sky to receive signals from multiple satellites.
- Antenna Type: Choosing the right type of GPS antenna (active or passive) based on the specific needs and signal conditions of the installation site.
- Environmental Conditions: GPS antennas must be durable and weather-resistant to withstand various environmental conditions, such as rain, snow, and extreme temperatures.
Conclusion: GPS antennas are an integral part of the telecom industry, providing the precise timing and synchronization needed for efficient network operation. By understanding their role and selecting the right type and placement, telecom operators can enhance network performance and reliability.